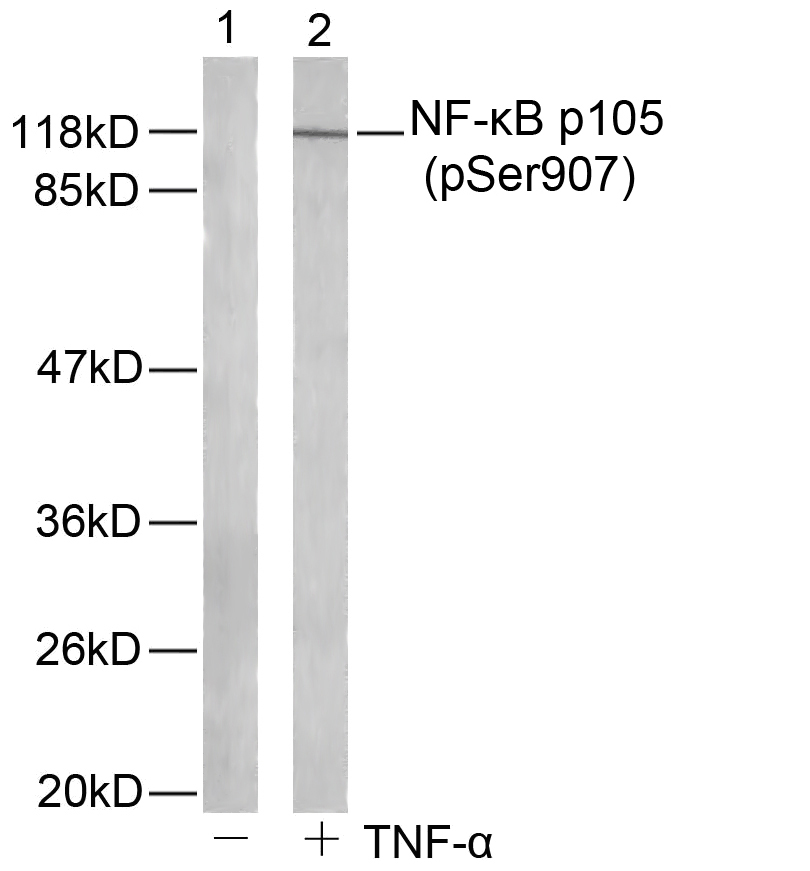

NF-kappa-B is a pleiotropic transcription factor present in almost all cell types and is the endpoint of a series of signal transduction events that are initiated by a vast array of stimuli related to many biological processes such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NF-kappa-B is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain-containing proteins RELA/p65, RELB, NFKB1/p105, NFKB1/p50, REL and NFKB2/p52 and the heterodimeric p65-p50 complex appears to be most abundant one. The dimers bind at kappa-B sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappa-B sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity. Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors, respectively. NF-kappa-B is controlled by various mechanisms of post-translational modification and subcellular compartmentalization as well as by interactions with other cofactors or corepressors. NF-kappa-B complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complexed with members of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor (I-kappa-B) family. In a conventional activation pathway, I-kappa-B is phosphorylated by I-kappa-B kinases (IKKs) in response to different activators, subsequently degraded thus liberating the active NF-kappa-B complex which translocates to the nucleus. NF-kappa-B heterodimeric p65-p50 and RelB-p50 complexes are transcriptional activators. The NF-kappa-B p50-p50 homodimer is a transcriptional repressor, but can act as a transcriptional activator when associated with BCL3. NFKB1 appears to have dual functions such as cytoplasmic retention of attached NF-kappa-B proteins by p105 and generation of p50 by a cotranslational processing. The proteasome-mediated process ensures the production of both p50 and p105 and preserves their independent function, although processing of NFKB1/p105 also appears to occur post-translationally. p50 binds to the kappa-B consensus sequence 5'-GGRNNYYCC-3', located in the enhancer region of genes involved in immune response and acute phase reactions. In a complex with MAP3K8, NFKB1/p105 represses MAP3K8-induced MAPK signaling; active MAP3K8 is released by proteasome-dependent degradation of NFKB1/p105.
Beg A.A., Baldwin A.S. Jr.Oncogene 9:1487-1492(1994)
Guizani-Tabbane L., Ben-Aissa K., Belghith M., Sassi A., Dellagi K.Infect. Immun. 72:2582-2589(2004)
Beinke S., Robinson M.J., Hugunin M., Ley S.C.Mol. Cell. Biol. 24:9658-9667(2004)
My Review
© 2017, AbSci All Rights Reserved. E-mail: info@abscitech.com
南京川博生物技术有限公司版权所有
苏B1-20150380 苏ICP备15009006号-1