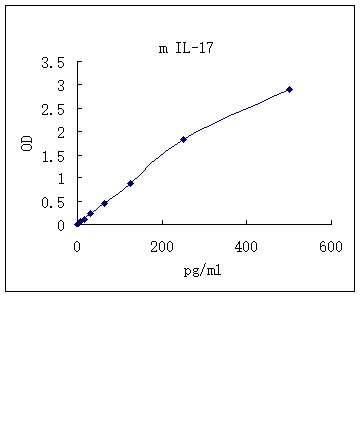
Detect Range: 7.8 - 500 pg/mL
Sensitivity: 4pg/mL
Sample Type: Cell culture supernatant, serum, plasma (EDTA, citrate, heparin)
Sample Volume: 20 uL
Assay Time: 3 hour
Detection method: Colorimetric
Mouse Interleukin 17 (IL-17; also known as IL-17A and CTLA-8) is a 21 kDa, variably glycosylated polypeptide that belongs to the IL-17 family of cytokines containing a cysteine-knot fold (1-3). Its sequence was originally isolated from an activated hybridoma created from the fusion of a mouse cytotoxic and rat T cell lymphoma cell line (2-5). It is synthesized as a 158 amino acid (aa) precursor that contains a 25 aa signal sequence and a 15 kDa, 133 aa mature segment (5). In both mouse and human, there is one conserved N-linked glycosylation site that likely contributes 5 kDa to its native molecular weight. IL-17A forms both a 35-38 kDa homodimer,and a 45-48 kDa heterodimer with IL-17F (6, 7). Mature mouse IL-17A is 61% and 89% aa identical to human and rat IL-17A, respectively (4, 5, 8). While rodent and human mature sequences show modest aa sequence identity, human IL-17 is active on both mouse and rat cells (5, 9). Cells known to produce IL-17 are the CD4+ Th17 T cells, Paneth cells, GR1+CD11b+ myeloid suppressor cells, CD27-γδ T cells, CD1+NK1.1- iNKT cells and CD3-CD4+ LTi-like cells(3, 5, 6, 10-12).
A high affinity receptor for mouse IL-17 has been reported, and appears to be a heteromultimer of IL-17RA and IL-17RC, likely in a 2:1 ratio (1). IL-17RA is a 130 kDa, type I transmembrane glycoprotein that bears no resemblance to members of the cytokine, TNF or immunoglobulin receptor superfamily (2, 10, 13). IL-17RC is also a type I transmembrane protein, approximately 90-95 kDa in size, that shares less than 30% aa identity with IL-17RA (14, 15). Both receptors are needed for IL-17A and IL-17A/F activity. The two receptors appear to form a functional association following ligand binding to IL-17RA (1, 16).
IL-17 is best known for its participation in the recruitment and survival of neutrophils (3, 10, 17,18). Its induction was initially described to be the result of antigen stimulation of dentritic cells, resulting in IL-23 secretion. In a TCR-independent event, IL-23 induces T cell production of IL-17(3). Once secreted, IL-17 in the bone marrow would seem to induce stromal/fibroblast expression of both G-CSF and SCF (membrane form), an effect that increases neutrophil differentiation and activation. IL-17 may complement this by directly blocking neutrophil apoptosis, promoting greater circulating neutrophil numbers (17). In the tissues, IL-17 seems to promote neutrophil extravasation, principally through its effects on macrophages and endothelial cells (EC). On macrophages, IL-17 induces TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 production (19).TNF-α and IL-1β then act on local ECs to induce G-CSF secretion, an effect that is potentiated by IL-17 (20). IL-17 further contributes to neutrophil influx by inducing EC CXC chemokine release and NO production, which may increase vascular permeability (3, 9). IL-17 effects are not limited to neutrophils. In synovial joints, IL-17 upregulates RANKL expression on osteoblasts. This provides a stimulus for osteoclast formation and subsequent bone resorption (18).
Gaffen, S. (2009) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 9:556.
Iwakura, Y. et al. (2008) Immunol. Rev. 226:57.
Kolls, J.K. and A. Linden (2004) Immunity 21:467.
Yao, Z. et al. (1995) J. Immunol. 155:5483.
Kennedy, J. et al. (1996) J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 16:611.
Liang, S.C. et al. (2007) J. Immunol. 179:7791.
Chang, S. and C. Dong (2007) Cell Res. 17:435.
Rouvier, E. et al. (1993) J. Immunol. 150:5445.
Miljkovic, D.J. Et al. (2003) Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 60:518.
Witowski, J. et al. (2004) Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 61:567.
Cua, D.J. and C.M. Tato (2010) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 10:479..
Shin, H.C. et al. (1998) Cytokine 10:841.
Yao, Z. et al. (1995) Immunity 3:811.
Haudenschild, D. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277:4309.
Toy, D. et al. (2006) J. Immunol. 177:36.
Hu, Y. et al. (2010) J. Immunol. 184:4307.
Schwarzenberger, P. et al. (2000) J. Immunol. 164:4783.
Yu, J.J. and S.L. Gaffen (2008) Front. Biosci. 13:170.
Jovanovic, D.V. et al. (1998) J. Immunol. 160:3513.
Numasaki, M. et al. (2004) Immunol. Lett. 95:97.
My Review
© 2017, AbSci All Rights Reserved. E-mail: info@abscitech.com
南京川博生物技术有限公司版权所有
苏B1-20150380 苏ICP备15009006号-1