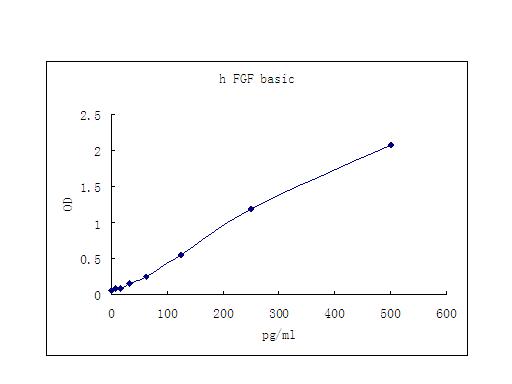
Detect Range: 7.8-500pg/ml
Sensitivity: 4pg/mL
Sample Type: Cell culture supernatant, serum, plasma (EDTA, citrate, heparin)
Sample Volume: 20 uL
Assay Time: 3 hours
Detection method: Colorimetric
FGF basic, also called FGF-2 (fibroblast growth factor-2) or HBGF-2 (heparin-binding growth factor-2), is the most intensively studied of the 22 mitogenic proteins of the FGF family (1-7). Family members share 35 - 60% amino acid (aa) identity, but only FGF acidic and basic lack signal peptides and are secreted by an alternate pathway.
The 18 kDa FGF basic isoform can be found in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus and is also the form that is secreted (8-10). Storage pools within the cell or on cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPG) are likely (2). Transcription from alternate start sites produces 21-23 kDa forms found only in the nucleus (8, 9). High and low molecular weight human FGF basic isoforms target the expression of different genes (9, 10). The 18 kDa human FGF basic sequence shares 97% and 99% aa identity with mouse/rat and bovine/ovine FGF basic, respectively (6, 7). Expression of FGF basic is nearly ubiquitous. However, disruption of the mouse FGF basic gene gives relatively mild cardiovascular, skeletal, and neuronal phenotypes, suggesting compensation by other FGF family members (11-15). Transgenic over-expression of FGF basic mainly influences development and mineralization of bone (4, 16, 17).
Four FGF tyrosine kinase receptors (FGF R) and their splice variants show differential binding of FGFs (1). FGF basic preferentially binds FGF R1c and 2c, for which it has picomolar affinity (1, 2). FGF basic also has a number of other binding partners that fine-tune FGF basic activities, according to their locations and quantities. FGF basic modulates such normal processes as angiogenesis, wound healing, tissue repair, learning and memory, and embryonic development and differentiation of heart, bone and brain (2 - 4). It is upregulated in response to inflammation via mediators such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-2, PDGF, and nitric oxide (2). Many human tumors express FGF basic, which may correlate with tumor vascularity (2, 5).
Mohammadi, M. et al. (2005) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16:107.
Presta, M. et al. (2005) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16:159.
Reuss, B. et al. (2003) Cell Tissue Res. 313:139.
Su, N. et al. (2008) Front. Biosci. 13:2842.
Grose, R. and C. Dickson (2005) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16:179.
Abraham, J.A. et al. (1986) EMBO J. 5:2523.
Kurokawa, T. et al. (1987) FEBS Lett. 213:189.
Claus, P. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:479.
Quarto, N. et al. (2005) Gene 356:49.
Kardami, E. et al. (2004) Cardiovasc. Res. 63:458.
Dono, R. et al. (1998) EMBO J. 17:4213.
Rosenblatt-Velin, N. et al. (2005) J. Clin. Invest. 115:1724.
Pellieux, C. et al. (2001) J. Clin. Invest. 108:1843.
Montero, A. et al. (2000) J. Clin. Invest. 105:1085.
Miller, D. et al. (2000) Mol. Cell. Biol. 20:2260.
Coffin, J.D. et al. (1995) Mol. Biol. Cell 6:1861.
Sobue, T. et al. (2005) J. Cell. Biochem. 95:83.
My Review
© 2017, AbSci All Rights Reserved. E-mail: info@abscitech.com
南京川博生物技术有限公司版权所有
苏B1-20150380 苏ICP备15009006号-1